Main Difference – Syntax vs. Semantics
Syntax and Semantics are two very important branches in linguistics. Linguistics is the study of language. Syntax is the study of the structure of sentence while semantics is the study of meaning in language. Therefore, the main difference between syntax and semantics is that syntax is concerned with structure while semantics is concerned with meaning.
What is Syntax
Syntax is a sub-discipline of linguistics that studies the structure of a sentence. It studies the set of rules, principles, and processes that rule the structure of sentences in any language. Here, the term structure of sentence refers to the word order. The meaning of a sentence can depend on the word order. For example, look at the two examples below.
Example 1
Because banana he is ate a hungry.
Example 2
He ate a banana because he is hungry.
The first example doesn’t make any sense, but if you look carefully, it contains the same words as the second example. The only difference exists in the word order. Therefore, the word order is a key element in the syntax.
However, this does not mean that syntax is about meaning. A sentence can be syntactically correct, yet have no meaning.
Colorless, green ideas sleep furiously.
Though the above sentence does not make any sense, it is syntactically correct. In this sentence, you can notice that adjectives, adverbs are placed in the correct order and, subject and verb are in accordance with each other.
In terms of syntactical categories, most sentences in any language can be divided as subject and predicate. Syntax usually studies sentences that have a clear inner division into subject and predicate. There are three types of sentences with this structure; simple sentence, compound sentence, and complex sentence.
In addition, words and phrases in a language can be categorized according to their function in a sentence. Syntactical classes of words are called parts of speech.

Syntax tree
What is Semantics
Semantics is a branch of linguistics that focuses on the study of meaning. It studies the meaning of words and language. Semantics study ways in which the meanings of words can be related to each other (synonyms, homophony, etc.), ways in which the meanings of sentences can be related to each other, and ambiguity. Ambiguity is one way of studying the meaning of language. A sentence is said to be ambiguous when it has more than one meaning. For example,
I saw the girl with binoculars.
This sentence has two meanings. One meaning is that I saw a girl while I was looking through the binoculars. The other is that I saw a girl who was using binoculars.
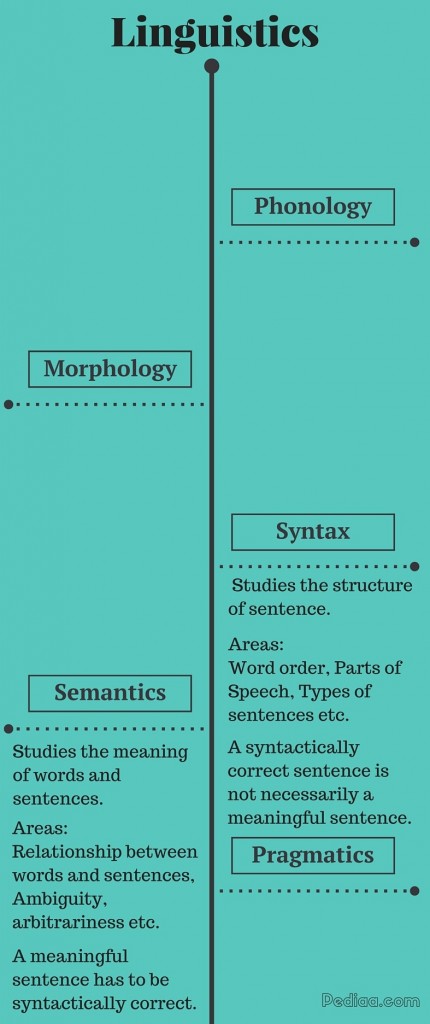
Difference Between Syntax and Semantics
Definition
Syntax: A sub-discipline of linguistic that studies the structure of a sentence.
Semantics: A sub-discipline of linguistic that studies the meaning of words and sentences.
Areas
Syntax: Word order, Parts of Speech, Types of sentences, etc. are studied in Syntax.
Semantics: Elements like ambiguity, the relationship between words and sentences based on meaning are studied in language.
Meaningful sentences
Syntax: A syntactically correct sentence is not necessarily a meaningful sentence.
Semantics: A meaningful sentence has to be syntactically correct.
Image Courtesy:
“Syntax tree” by Aaron Rotenberg – Own work. (Public Domain) via Wikimedia Commons